What Is Low Code Automation? Use Cases, Tips and Tools

In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses can’t afford to wait months for custom software builds. They need solutions now. That’s why over 70% of enterprises are turning to low-code automation by 2026 to build apps faster, cut manual work, and empower teams without deep coding skills. From small startups to global giants, organizations are using visual, drag‑and‑drop tools to transform how work gets done.
In this article, we’ll break down what low-code automation really means, explore real-world use cases and examples, review top tools, and share actionable insights to help you implement it effectively.
What Is Low-Code Automation?
Low-code automation is the practice of building and automating business processes using platforms that require little to no traditional coding. These tools use visual interfaces, like drag and drop builders, along with pre-built logic blocks and plug and play connectors to simplify development.
That means your operations manager or HR lead, without any developer training, can create automated workflows that used to take weeks of coding.
At its core, low-code automation bridges the gap between business needs and technical delivery. It empowers non-developers, often called citizen developers, to solve real problems fast while still giving IT the control and scalability they need.
For example, instead of submitting a paper form for leave approval, an employee can trigger a fully automated workflow with status tracking, email updates, and manager approvals. All of it can be built by someone in HR, not IT.
The big idea is simple. Automation shouldn’t be locked behind code. Low-code platforms open the door to faster innovation, better collaboration, and smarter work across your entire organization.
How Low-Code Automation Works
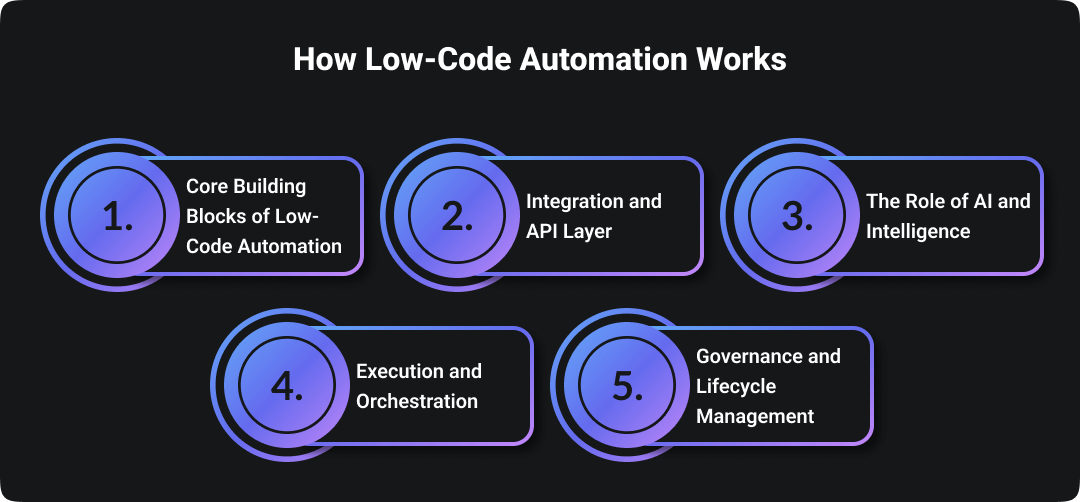
Low-code automation works by giving users a visual, modular way to build and deploy automated workflows. Instead of writing complex code, users create logic through drag and drop components, connecting data, actions, and systems using prebuilt elements.
Let’s break down the core components that make it work.
1. Core Building Blocks of Low-Code Automation
At the heart of every low-code automation platform are five essential components:
- Workflow Engine: This is where processes are defined and executed. You set the steps, conditions, and paths a task should follow. Whether it’s sending an email, assigning a task, or updating a database, the engine runs it all behind the scenes.
- Connectors: These allow the platform to talk to other systems like CRMs, ERPs, spreadsheets, or databases. You can plug into tools like Salesforce, Slack, Gmail, or custom APIs without writing new code.
- Data Modeling: Every app needs to work with data. Low-code platforms let you define data structures visually like creating tables, fields, or relationships without needing SQL or database design experience.
- User Interface (UI): You can build forms, dashboards, or entire front-end applications using pre-designed components. No front-end coding required. Just drag, drop, and adjust.
- Decision Logic: Use conditions, rules, and triggers to define how your automation behaves. For example, “If invoice amount is over $5,000, route to finance head for approval.”
These components work together to create intelligent, flexible workflows that align with your business needs.
2. Integration and API Layer
Low-code platforms thrive on their ability to integrate. They come with built-in connectors and support for open APIs, making it easy to link different systems across your organization.
Let’s say you want to create a customer onboarding process. With low-code, you can pull customer data from your CRM, send it to a document management system for contract generation, and notify your support team in Slack. All without writing a single API call.
If a needed integration doesn’t exist, you can often create custom connectors or plug into legacy systems using REST, SOAP, or even database queries.
3. The Role of AI and Intelligence
Many modern low-code platforms are now embedding AI to make automations smarter.
For example:
- AI-powered decisioning: Recommend the best next action based on data.
- Natural language processing (NLP): Let users build flows by typing what they want to automate.
- Predictive analytics: Flag delays or issues before they happen.
AI doesn’t replace logic but enhances it by making automation more adaptive and context-aware.
4. Execution and Orchestration
Once your automation is built, the platform handles execution across all connected systems. This orchestration ensures tasks happen in the right order, with real-time status tracking.
For example:
- If a form is submitted, the system might trigger an approval flow, send an email, update a CRM, and create a task in your project tool automatically and instantly.
Execution engines also manage retries, error handling, and conditional branching, ensuring the workflow is resilient and reliable.
5. Governance and Lifecycle Management
Enterprise-grade platforms come with built-in governance tools to keep your automation efforts secure and compliant.
- Version Control: Roll back changes or test new versions before going live.
- Monitoring: Track performance metrics, identify bottlenecks, and see who’s building what.
- Audit Trails: Log every step in the process to ensure transparency and accountability.
- User Roles & Permissions: Define who can build, approve, or deploy workflows.
This governance layer is what allows both citizen developers and IT teams to work together without losing control.
Also Read: WeWeb Alternatives
Benefits of Low-Code Automation
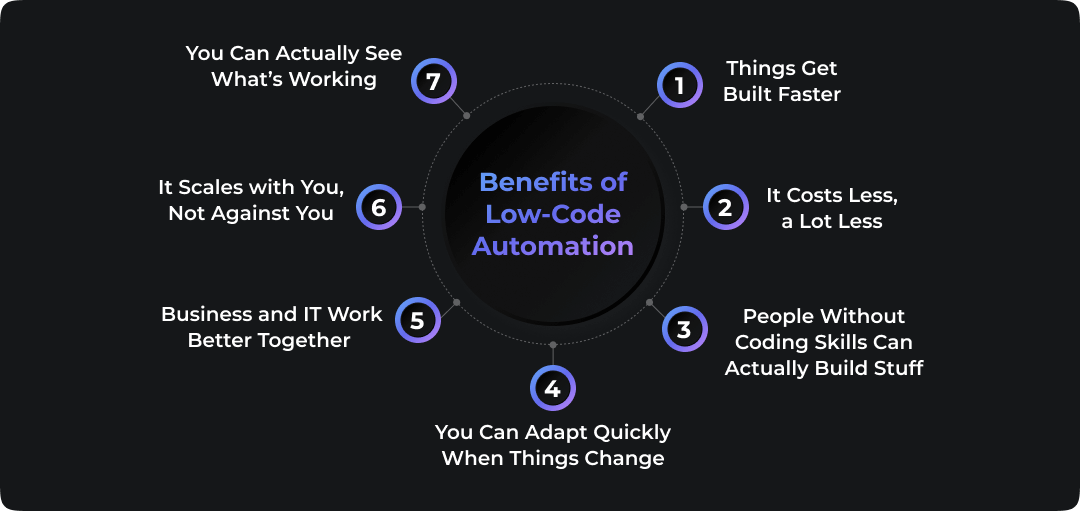
Low-code automation isn’t just a trend. It’s changing the way businesses work by making it easier, faster, and cheaper to build what you need. Whether you’re trying to speed up internal processes or reduce your team’s workload, low-code tools are making that a lot more possible.
1. Things Get Built Faster
Let’s face it. Traditional development takes time. Between planning, coding, testing, and approvals, even simple apps can take months to go live.
With low-code, the process moves faster. Teams can build working prototypes in a few days using visual builders and ready-made components. No need to wait for the next dev sprint. You make the changes, test them, and publish.
This isn’t just about convenience. Moving quickly gives you a real edge when customer needs shift or new ideas come up.
2. It Costs Less, a Lot Less
Hiring a team of experienced developers or outsourcing big projects is expensive. Low-code helps cut that cost by letting your existing team do more with less support.
Business users can build workflows themselves, while IT oversees the structure and security. You don’t have to depend on external vendors every time you want a small feature added.
For many companies, this means saving thousands of dollars and trimming weeks off the delivery timeline.
3. People Without Coding Skills Can Actually Build Stuff
One of the biggest wins with low-code is that it gives power to the people who are closest to the problem.
Instead of submitting a ticket and waiting weeks, your HR manager or operations lead can build their own workflow to fix the issue. No coding needed, just a bit of training and the right tool.
This kind of hands-on ownership makes teams more agile and creative. They’re not just following the process anymore. They’re improving it.
4. You Can Adapt Quickly When Things Change
Business moves fast. Whether it’s a new compliance rule or a shift in customer behavior, you often need to update processes on short notice.
With low-code, that’s not a big deal. You can adjust forms, add steps to a workflow, or connect new tools without starting from scratch or waiting on developers.
This flexibility helps you stay ahead of changes instead of scrambling to catch up.
5. Business and IT Work Better Together
One of the biggest pain points in many companies is the disconnect between business users and IT.
Low-code brings both sides to the table. Business users define the process, and IT makes sure it’s scalable and secure. Everyone can work in the same environment, using the same language or at least close enough.
That means fewer misunderstandings and a smoother path from idea to execution.
6. It Scales with You, Not Against You
You might start small with just a few automated tasks, but low-code platforms are built to grow. As your needs get more complex, the platform can support more users, more data, and more advanced logic.
With built-in governance tools like access control, audit logs, and approval layers, you don’t have to sacrifice control to scale up.
7. You Can Actually See What’s Working
Once you automate a workflow, you get visibility into how things are performing.
Who’s using it? Where are the delays? What’s getting stuck?
Low-code platforms come with dashboards and reporting tools that show exactly what’s happening behind the scenes. That means you’re not guessing anymore. You’re making decisions based on real data.
Also Read: 10 Best Codev Alternatives and Competitors
Tips for Implementing Low-Code Automation
Low-code automation can make your business faster, leaner, and more efficient. But success depends on how you roll it out. It’s not just about picking the right tool. It’s about building smart habits from the start. Here are five tips to help you do it right.
1. Start with Repetitive Tasks That Drain Time
Every team has those tasks that feel like busywork. Things like entering the same data over and over, handling simple approvals, or forwarding emails between departments.
These are exactly the kinds of processes that low-code tools can handle with ease. By starting here, you can create quick wins, boost team morale, and free up time for more important work.
2. Bring Both Business and IT to the Table Early
Low-code works best when business and IT teams build together. Business users understand the real pain points. IT knows how to keep systems secure, connected, and stable.
When both sides are involved from day one, the final solution is more likely to work well and get adopted faster. You avoid miscommunication, reduce rework, and speed up delivery.
Pair a business lead with an IT partner for each project. Let them co-own the outcome.
3. Choose a Platform That Fits Your Actual Needs
Not every low-code platform is built the same. Some are great for simple workflows. Others are designed for large-scale enterprise automation.
Before you commit, think about your goals. Do you need strong integrations? Built-in analytics? Easy drag-and-drop design? Start with what your team actually needs, not just what’s trending.
Try out a few platforms before deciding. A hands-on trial will tell you more than a product demo.
4. Start Small, Then Scale Gradually
Trying to automate everything at once is a recipe for stress. It’s better to begin with one focused project that delivers clear results.
Pick something that’s annoying but manageable. Build a simple workflow. Show how it improves speed or accuracy. Once people see the benefit, they’ll be more open to expanding automation across the company.
Example: Automating IT access requests is a small project that makes an immediate impact.
5. Keep Improving After You Launch
Launching automation is just the beginning. The real value comes from watching how it performs and making it better over time.
Use built-in analytics to track what’s working. Ask users for feedback. Adjust steps that cause delays. Most low-code tools let you update workflows without starting from scratch.
Also Read: 5 Best Appsmith Alternatives and Competitors
Real-World Examples of Low-Code Automation
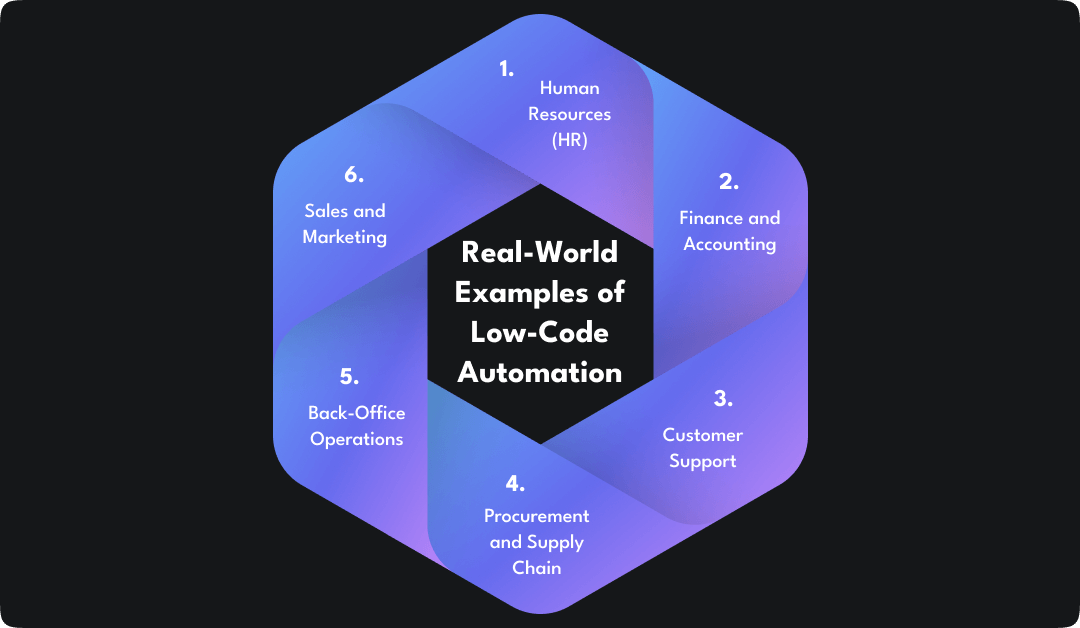
Low-code automation isn’t just theory. It is delivering real results across departments in organizations of all sizes. Below are practical examples of how businesses are using it to eliminate inefficiencies, reduce manual work, and improve speed.
1. Human Resources (HR)
Modern HR teams are turning to low-code automation to make their work smoother and faster. Instead of handling piles of onboarding paperwork or sending multiple reminder emails, HR can use automated workflows to collect documents, assign tasks, and update employee records instantly. The same applies to leave requests. Employees submit a form, managers approve it, and the system automatically updates attendance data.
2. Finance and Accounting
Finance departments often spend hours handling repetitive, time-consuming tasks. With low-code tools, invoice processing becomes simple. The platform can pull data from invoices, verify it against purchase orders, and send it for approval automatically. Expense claims can also be automated. Employees upload receipts, and the system checks them for policy compliance before forwarding them for payment.
3. Customer Support
Customer support teams handle a constant flow of requests. Low-code automation helps by categorizing tickets, assigning them to the right team, and sending acknowledgment messages automatically. This reduces manual effort and ensures customers get faster responses. Managers also gain real-time visibility into ticket volumes and resolution rates.
4. Procurement and Supply Chain
Procurement teams often deal with complex approval processes and vendor documentation. Low-code platforms make it easier to create workflows that handle purchase order approvals and vendor onboarding automatically. For example, when a new supplier registers, the system routes their details through finance, legal, and compliance before granting access. It cuts waiting times and improves coordination between departments.
5. Back-Office Operations
Internal operations like IT support, access requests, and document sign-offs can be fully automated. Employees simply fill out a digital form, and the workflow automatically routes it for approval and completion. This not only saves time but also keeps records organized for future reference.
6. Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing teams benefit greatly from low-code automation. It helps them manage leads, automate follow-ups, and streamline campaign approvals. For instance, when a new lead fills out a website form, the system can assign it to a sales rep, trigger a welcome email, and update the CRM instantly. Marketing teams can also track campaign performance and approvals without juggling spreadsheets.
Also Read: Base44 Alternatives: 5 AI App Builders You Should Try
Industry-Specific Use Cases of Low-Code Automation
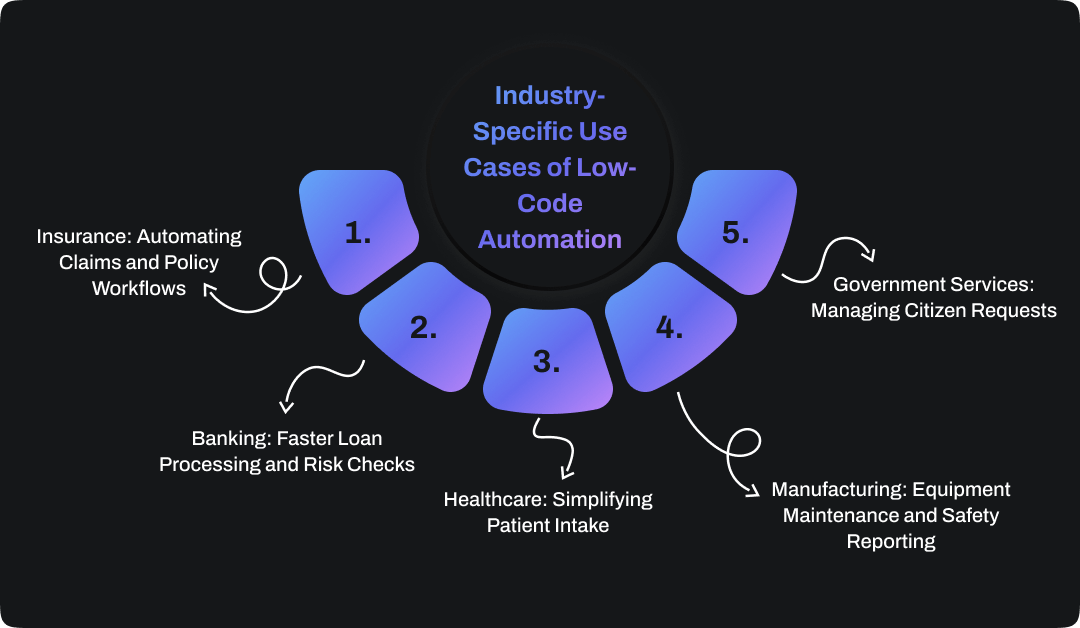
Low-code automation is not limited to internal workflows. It’s making a measurable difference across entire industries. From healthcare to government, organizations are using it to streamline operations, improve compliance, and deliver better service.
1. Insurance: Automating Claims and Policy Workflows
Insurance companies deal with lots of paperwork and slow-moving processes. With low-code automation, they can streamline claims handling by creating workflows that check policy coverage, request missing documents, and route cases to the right adjusters. This not only speeds up claim resolution but also helps improve customer satisfaction.
2. Banking: Faster Loan Processing and Risk Checks
Banks often face bottlenecks when processing loan applications. Low-code tools allow teams to automate everything from document collection and credit scoring to approval workflows. For example, once a customer submits a loan request, the system can trigger background checks, notify risk teams, and send real-time status updates to the applicant.
3. Healthcare: Simplifying Patient Intake
Hospitals and clinics can use low-code platforms to make patient onboarding smoother. Instead of filling out physical forms, patients can complete digital versions that instantly sync with hospital databases. Automation can also help validate insurance details, send reminders, and flag missing information before the appointment even starts.
4. Manufacturing: Equipment Maintenance and Safety Reporting
In factories and field operations, downtime is expensive. Low-code solutions can automate equipment maintenance schedules, safety inspections, and repair requests. For instance, if a technician reports a malfunction, the system can automatically notify the right team, assign a technician, and track the repair status with no phone calls or spreadsheets needed.
5. Government Services: Managing Citizen Requests
Public agencies are using low-code automation to improve how they handle service requests, permits, and case files. For example, a city government can automate pothole reports by letting citizens submit requests online, automatically routing them to the right department, and sending updates when the issue is resolved. It cuts down paperwork and speeds up response times.
Top 3 Low-Code Automation Tools That You Should Try Now
1. Vitara

Vitara is an AI-powered low-code platform that helps you build full-stack web apps by simply describing what you want. Whether it’s a login page, a custom dashboard, or a full internal tool, you type it in plain English and Vitara generates the frontend, backend, and even the APIs for you.
It’s designed for people who want to move fast without writing boilerplate code or setting up complex infrastructure.
Key Features
- Natural language prompts: Describe the app or feature and get instant working code
- Full-stack generation: Build UI, backend logic, and database structure in one go
- Live editing and real-time preview: Make changes and see updates instantly
- Code export: Download and host the code wherever you want
- No installation needed: Everything runs in the browser
Pros
- Easy to use, even for non-developers
- Great for building MVPs, internal tools, or dashboards
- Saves hours of setup and repetitive coding
- Real, editable code with no platform lock-in
- Clean, fast interface that feels modern
Cons
- Focused on web apps only, not ideal for mobile app development
- May need manual refinement for complex backend logic
- Smaller community and fewer tutorials compared to older platforms
Pricing
- Free: Try core features with 5 messages/day and 25 messages/month
- Starter ($20/month): Great for small teams, includes private projects and 100 messages/month
- Elevate ($50/month): Higher usage limits with 250 messages/month and professional features
- Enterprise: Custom plan with advanced support, usage flexibility, and team collaboration features
2. Kissflow
Kissflow is a unified low-code platform focused on workflow and business process automation. It helps teams design, automate, and manage processes and apps without heavy coding. It’s built for both business users and IT to collaborate on process design, integration, and app delivery.
Key Features
- Process designer Visual drag‑and-drop canvas to model workflows
- Form builder Create dynamic forms with rules, validation, and conditional logic
- Integration connectors Connect to databases, APIs, and third‑party tools
- Reports & dashboards Track performance, bottlenecks, and process metrics
- User role & access control Manage permissions, approvals, and security
Pros
- Strong tool for business process automation and workflow orchestration
- Easy to use UI, especially for non-technical users
- Good balance between flexibility and structure
- Built-in analytics for process monitoring
- Supports collaboration between IT and business teams
Cons
- May not fit highly complex, custom logic use cases without extensions
- Some advanced integrations require custom work or developer support
- Pricing details are less transparent publicly
Pricing
- Free: Core features to get you started
- Basic: For small teams seeking workflow automation
- Professional: Mid-tier plan with more apps, users, and integrations
- Enterprise: Custom plan offering full scale, premium support, and advanced features
3. Microsoft Power Apps
Microsoft Power Apps is a low-code platform that allows you to build web and mobile applications using drag-and-drop tools and built-in logic. It’s tightly integrated with Microsoft 365, SharePoint, Dynamics, and Azure, making it an excellent choice for businesses already using Microsoft products.
Key Features
- Canvas and model-driven app options to suit different use cases
- Prebuilt connectors for SharePoint, Excel, SQL, Dynamics, and many other services
- Dataverse for secure and structured data storage
- Workflow automation and business logic using Power Fx
- Responsive design for use across desktop, tablet, and mobile
- AI Builder integration to add features like form recognition or prediction
Pros
- Seamless integration with Microsoft tools like Teams and Office 365
- Suitable for both business users and developers
- Strong for building internal business apps and data dashboards
- Enterprise-ready security and governance controls
- Scales well as your needs grow
Cons
- Premium features and connectors can get expensive
- Performance may drop with large datasets or complex workflows
- Limited real-time collaboration on app building
- Learning curve for advanced formulas in Power Fx
- Managing app sprawl and permissions gets harder as usage increases
Pricing
- Free / Developer Plan: Build, test, and explore features in a personal dev environment
- Per App Plan ($5/user/app/month): Run one app or portal per user
- Per User Plan ($20/user/month): Access unlimited apps and portals
- Enterprise: Custom pricing for organizations with broader needs and support requirements
Also Read: A Complete Guide to Top Vibe Coding Tools
Conclusion
Low-code automation is no longer just a buzzword. It’s a practical, proven way to build faster, reduce manual work, and empower teams to solve problems without waiting on developers. Whether you’re streamlining internal operations or launching new tools, the right low-code platform can help you move from idea to execution with less friction.
The key is to start small, choose a platform that fits your needs, and involve both business and IT from the start. With the right approach, low-code isn’t just a shortcut it’s a smarter way to work.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is low-code automation?
Low-code automation is the faster, easier way to build and automate business processes without needing to write tons of code. Instead of waiting weeks or months for developers to build something from scratch, teams use visual drag-and-drop tools to create workflows, apps, and internal tools in a fraction of the time.
Which teams or departments benefit most from low-code automation?
Almost every team can benefit but the biggest wins usually start with the departments that are drowning in repetitive, manual tasks. HR, Finance, Customer Support, Procurement, Sales, and IT are often the first to see serious impact.
- HR teams use low-code to automate onboarding, leave requests, and employee record updates no more chasing emails or paper forms.
- Finance departments streamline invoice approvals, expense claims, and data validation, saving hours every week.
- Customer Support automates ticket assignment, responses, and tracking so customers get help faster.
- Procurement and supply chain teams handle vendor onboarding and purchase order approvals without the back-and-forth.
- Sales and Marketing automate lead follow-ups, campaign approvals, and CRM updates—giving reps more time to close deals.
- Back-office operations and IT use it for things like access requests, asset tracking, and workflow routing to keep everything running smoothly.
What are the core benefits of low-code automation?
Here’s why more teams are turning to low-code automation to get work done faster and smarter:
- Faster development: Build apps and workflows in days, not months.
- Lower costs: Reduce the need for full-time developers and expensive custom builds.
- Empowers non-technical users: Business teams can create solutions without coding.
- Improved agility: Easily adapt workflows as business needs change.
- Stronger collaboration: Business and IT work together in the same environment.
- Scales with you: From small tasks to enterprise-wide processes, it grows with your needs.
- Better visibility: Built-in dashboards show real-time performance and bottlenecks.
How do low-code tools integrate with existing systems like CRMs or ERPs?
Low-code tools connect easily with CRMs, ERPs, and other apps using prebuilt connectors and APIs. You can sync data, trigger actions, and automate workflows without custom coding. It’s fast, flexible, and works with the systems you already use.
Can low-code automation handle complex workflows and approvals?
Yes, low-code automation can manage complex workflows with layered approvals and conditional logic. It’s built to handle real business scenarios without needing custom code.
Which low-code tools are best suited for startups vs. enterprises?
For startups, you’ll want a low-code tool that emphasizes speed, simplicity, and cost efficiency, something that lets you launch an MVP fast and iterate without heavy infrastructure.
For enterprises, the focus shifts to governance, scalability, deep integrations, and enterprise-grade security. Platforms built for larger organizations typically include features like role-based access, audit trails, and full lifecycle management.
How do I choose the right low‑code platform for my team’s needs?
To choose the right low-code platform, focus on your team’s goals, technical skill level, and integration needs. Make sure the tool is easy to use, works with your existing systems, and can scale as you grow. Start with a small project to test fit before going all in.
What are the top low-code automation tools?
Some of the best low-code automation tools right now are:
- Vitara – Great for building full-stack web apps just by describing what you want. It’s fast, AI-powered, and perfect for MVPs or internal tools.
- Kissflow – Ideal for teams focused on workflow automation. Its drag-and-drop builder and process management features make it easy for both business and IT users.
- Microsoft Power Apps – A strong choice if you're already using Microsoft 365. It helps you build both web and mobile apps with built-in logic and tight integration across the Microsoft ecosystem.



